principle of barfoed test|Barfoed’s Test: Principle, Reagents & Result Interpretation : Tagatay Barfoed’s test is a chemical test used for detecting the presence of monosaccharides. It is based on the reduction of cupric (II) acetate to cuprous (I) oxide (Cu 2 O), which forms a brick-red precipitate. VSiN is dedicated to improving your college basketball betting experience by providing college basketball odds today, along with all the relevant news and information. Stay ahead of the game with up-to-date NCAA odds and spreads, ensuring you're well-equipped to make better wagers. Check out the latest Vegas basketball odds today with VSiN.
PH0 · Experiment
PH1 · Carbohydrates
PH2 · Barfoed’s Test: Principle, Reagents & Result Interpretation
PH3 · Barfoed’s Test: Principle, Procedure, Reaction, and Result
PH4 · Barfoed’s Test: Objective, Principle, Reagents,
PH5 · Barfoed’s Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results And
PH6 · Barfoed’s Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results
PH7 · Barfoed’s Test
PH8 · Barfoed's test
PH9 · Barfoed's Test
Buy Mobile Chargers at Low Price in Qatar and Doha - Get Free Home Delivery Inside Doha - Also, Enjoy Free Shop Pickup to See and Buy Product. . Fujifilm Mirrorless Camera; Fujifilm X-A5 Mirrorless Camera with 15-45mm Lens – Pink. QR 1299 . Upon. Stock Availability .
principle of barfoed test*******The Barfoed reagent is made up of copper acetate in a dilute solution of acetic acid. Since acidic pH is unfavorable for reduction, monosaccharides, which are strong reducing agents, react in about 1-2 min. However, the reducing disaccharides take a . Tingnan ang higit paImage Reaction Source: Chemistry Learner, Created with BioRender.com. 1. The presence of red precipitate detects the presence of reducing monosaccharides in the sample. 2. If the color appears within the first few minutes, the sample contains reducing . Tingnan ang higit paBarfoed’s test is a chemical test used to detect the presence of monosaccharides which detects reducing monosaccharides in the presence of disaccharides. This reaction . Tingnan ang higit paBarfoed’s test is a chemical test used for detecting the presence of monosaccharides. It is based on the reduction of cupric (II) acetate to cuprous (I) oxide (Cu 2 O), which forms a brick-red precipitate.
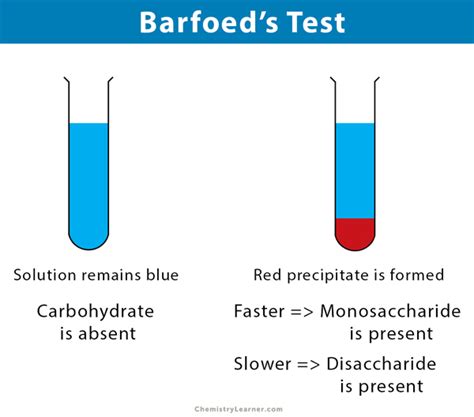
Barfoed’s test is a biochemical test used to detect monosaccharide (reducing) sugars in solution. The technique was devised by a Swedish physician C. .principle of barfoed testBarfoed’s test is a chemical test used to distinguish between monosaccharides and disacchar ides according to their capacity to generate copper(I) oxide (Cu 2 O) in an . Principle. Barfoed’s test reaction is based on the reduction of cupric acetate by reducing monosaccharides and reducing disaccharides. Reduction of cupric .Barfoed's test is a chemical test used for detecting the presence of monosaccharides. It is based on the reduction of copper(II) acetate to copper(I) oxide (Cu 2 O), which forms . Principle of Barfoed’s test: Barfoed’s test is used for distinguishing monosaccharides from reducing disaccharides. Monosaccharides usually react in about 1-2 minute while the reducing .
An unknown carbohydrate gave a red precipitate when tested with Fehling’s reagent, turned red when reacted with Seliwanoff’s reagent, and quickly gave a red .A biochemical test to detect monosaccharide (reducing) sugars in solution, devised by the Swedish physician C. T. Barfoed (1815–99). Barfoed's reagent, a mixture of ethanoic .Shows positive test for: Reducing monosaccharides Reactions: Reducing monosaccharides are oxidized by the copper ion in solution to form a carboxylic acid .Barfoed’s test: A chemical test known as the Barfoed's test is used to identify the presence of monosaccharides and can identify reducing monosaccharides when disaccharides are present. Disaccharides might be used in this reaction, although it would proceed extremely slowly. A diluted acetic acid solution of copper acetate Cu (CH 3 .

How to perform the test: One ml of a sample solution is placed in a test tube. Three ml of Barfoed's reagent (a solution of cupric acetate and acetic acid) is added. The solution is then heated in a boiling water bath for three minutes. A positive test is indicated by: The formation of a reddish precipitate within three minutes.
Barfoed’s Test: Principle, Reagents & Result Interpretation Principle: Barfoed’s test is a simple and rapid test used for the identification of monosaccharides. In this test, a sample is heated with Barfoed’s reagent (a mixture of copper acetate and acetic acid) in a boiling water bath. Monosaccharides (such as glucose, fructose, and galactose) reduce the copper ions in the reagent to form a red .
Principle: In Barfoed’s test, the copper ion in the solution oxidizes the reducing monosaccharide to form a carboxylic acid and copper (I) oxide, resulting in the formation of a red coloured precipitate. Procedure: 1 mL of the solution to be tested + 3 mL of freshly prepared Barfoed’s reagent; Place test tubes in a boiling water bath for 3 . This is the video on barfoed's test which is done for the detection of monosaccharides along with live demonstrationSubscribe my channel from - http://www.y.Principle. This test is based on the reaction of alpha-naphthol with carbohydrates in the presence of sulfuric acid. The sugars react with alpha-naphthol in an acidic environment to form purple-colored furfural or hydroxymethylfurfural derivatives. . Barfoed’s Test. It is a differentiating test to distinguish between monosaccharides and .
principle of barfoed test Barfoed’s Test: Principle, Reagents & Result InterpretationMolisch’s Test Procedure. 2-3 drops of Molisch’s reagent must be added to a small amount of the analyte in a test tube and mixed well. Now, a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid must be added drop-wise along the walls of the test tube to facilitate the formation of a layer and avoid mixing. The development of a purple ring at the layer . Procedure of Fehling’s Test. Take 1 ml of a given sample in a clean, dry test tube. The concentration of the test samples should be 5% (w/v). Take control of 1 ml of distilled water in another tube. Add about 2-3 drops of Fehling’s reagent to both the tubes and mix them in a vortex. Keep the test tubes in the water bath for 1-2 minutes.
Piso Wifi provides their users with super-fast internet speeds through a broadband connection, allowing them to browse the web and watch videos with the speed that no other providers can provide. Significance of Piso WiFi: Customer satisfaction is one of the major benefits of using Piso WiFi's services. Their user interface makes it easy for .
principle of barfoed test|Barfoed’s Test: Principle, Reagents & Result Interpretation